Yolo를 이용해서 여러명의 얼굴을 모자이크 처리하기
나 빼고 다 모자이크 처리해야 하는데…
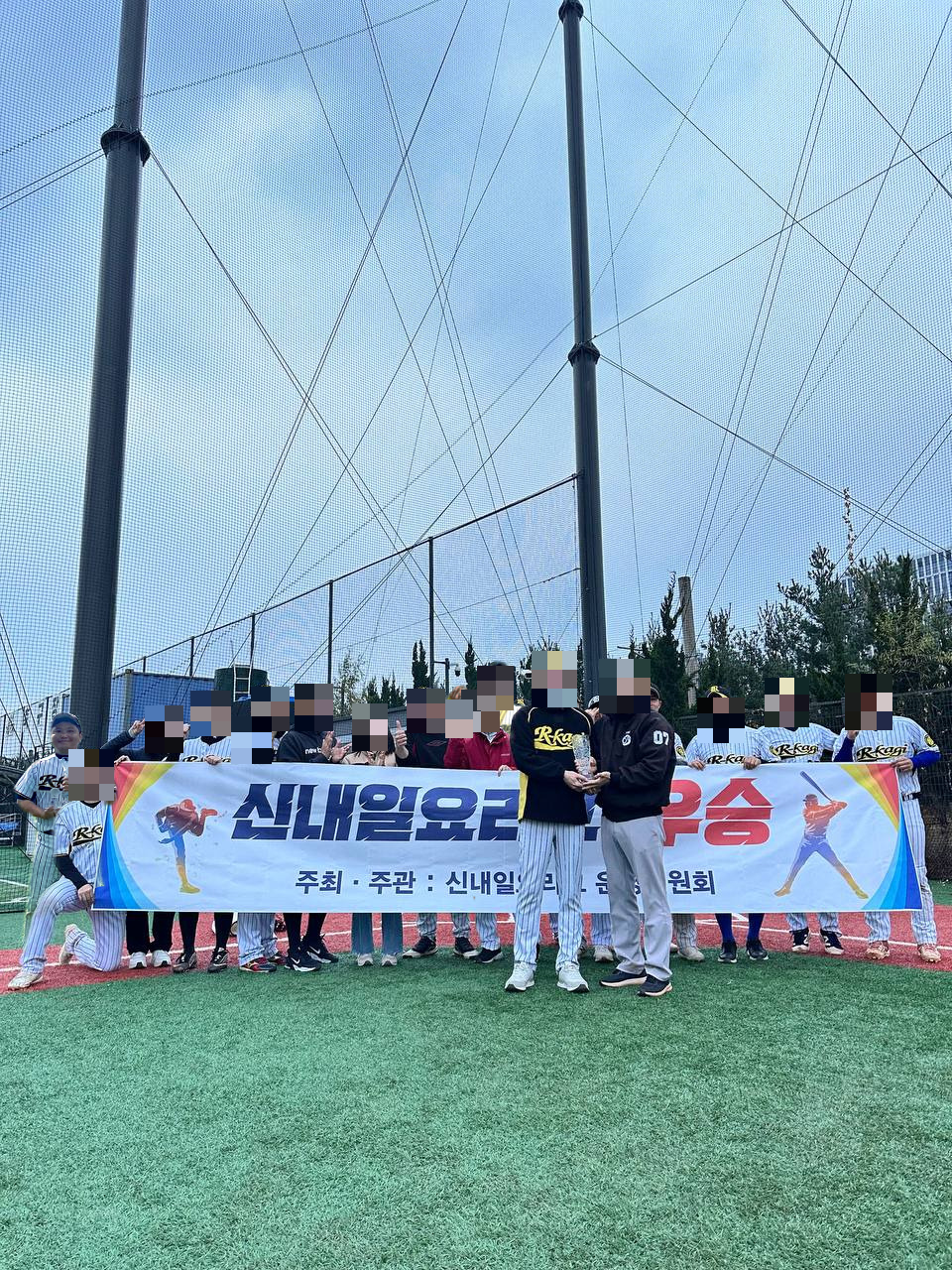
- 지난 시간에 배경제거 AI 모델을 이용해서 단체사진 속에 저의 사진을 합성해 봤는데요
- 결과물을 블로그에 올리려다 보니, 사진에 나오신 분들의 얼굴을 모자이크 처리해야 겠더라구요
- 처음에는 포토피아로 하나하나 블럭 지정해서 할까 하다가 그냥 코파일럿으로 코드 하나 만들어서 돌리는게 더 편하겠더군요
- 그런데 또 제 사진은 굳이 모자이크 처리하지 않고 싶은거에요…
광고를 클릭해주시면 블로그운영에 큰 힘이 됩니다.
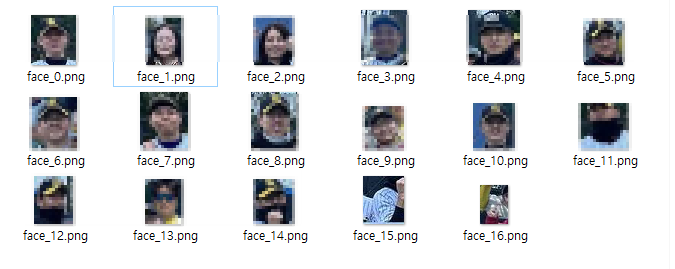
모자이크 처리 할 얼굴을 골라서 해보자
- 얼굴인식 모델은 yolo를 이용했구요
- 프로그램을 돌리면 디텍팅한 얼굴을 하나씩 파일로 저장하게 했습니다.
- 그럼 이제 여기서 제 사진의 번호만 빼고 selection 옵션에 입력해서 모자이크 처리하게 할건데요
- 위 사진을 보시면 아시겠지만, 정확도가 100%는 아니라서 얼굴이 아닌 것도 디텍팅 합니다.
- 굳이 이런것도 모자이크 처리하는데 넣을 필요는 없겟죠.
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from ultralytics import YOLO
def ensure_dir(path):
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
def detect_faces_yolov8(image_np, model_path='yolov8x-face-lindevs.pt', conf=0.15):
# YOLOv8-face 모델 로드 및 추론
model = YOLO(model_path)
results = model(image_np, conf=conf)
faces = []
for r in results:
for box in r.boxes.xyxy.cpu().numpy():
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box[:4]
x, y, w, h = int(x1), int(y1), int(x2 - x1), int(y2 - y1)
faces.append((x, y, w, h))
return faces
def save_faces(image_np, faces, output_dir, expand_ratio=0.8):
ensure_dir(output_dir)
h_img, w_img = image_np.shape[:2]
for idx, (x, y, w, h) in enumerate(faces):
# 영역 확대
x_exp = max(0, int(x - w * expand_ratio / 2))
y_exp = max(0, int(y - h * expand_ratio / 2))
w_exp = min(w_img - x_exp, int(w * (1 + expand_ratio)))
h_exp = min(h_img - y_exp, int(h * (1 + expand_ratio)))
face_img = image_np[y_exp:y_exp+h_exp, x_exp:x_exp+w_exp]
face_pil = Image.fromarray(face_img)
face_pil.save(os.path.join(output_dir, f"face_{idx}.png"))
def mosaic_faces(image_np, faces, selection, expand_ratio=0.8):
out_img = image_np.copy()
h_img, w_img = image_np.shape[:2]
# selection이 'all'이면 모든 얼굴 인덱스 선택
if selection == 'all':
selected_indices = set(range(len(faces)))
else:
selected_indices = set(selection)
for idx, (x, y, w, h) in enumerate(faces):
if idx in selected_indices:
# 영역 확대
x_exp = max(0, int(x - w * expand_ratio / 2))
y_exp = max(0, int(y - h * expand_ratio / 2))
w_exp = min(w_img - x_exp, int(w * (1 + expand_ratio)))
h_exp = min(h_img - y_exp, int(h * (1 + expand_ratio)))
face = out_img[y_exp:y_exp+h_exp, x_exp:x_exp+w_exp]
small = cv2.resize(face, (max(1, w_exp//15), max(1, h_exp//15)), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
mosaic = cv2.resize(small, (w_exp, h_exp), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
out_img[y_exp:y_exp+h_exp, x_exp:x_exp+w_exp] = mosaic
return out_img
def main(input_path, output_dir, selection_str=None, model_path='yolov8x-face-lindevs.pt'):
# PIL로 이미지 로드 (jfif 등 지원)
pil_img = Image.open(input_path).convert('RGB')
image_np = np.array(pil_img)
faces = detect_faces_yolov8(image_np, model_path)
print(f"얼굴 검출 수: {len(faces)}")
# 1. 얼굴 부분만 따로 저장
save_faces(image_np, faces, output_dir)
# 2. 선택된 얼굴만 모자이크 처리
if selection_str:
if selection_str.strip().lower() == 'all':
selection = 'all'
else:
selection = [int(s) for s in selection_str.split(',') if s.strip().isdigit()]
mosaic_img = mosaic_faces(image_np, faces, selection, expand_ratio=0.8)
mosaic_pil = Image.fromarray(mosaic_img)
mosaic_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "mosaic.png")
mosaic_pil.save(mosaic_path)
print(f"모자이크 이미지 저장: {mosaic_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--input", type=str, required=True, help="입력 이미지 파일 경로 (jpg, png, jfif 등)")
parser.add_argument("--output", type=str, required=True, help="출력 폴더 경로")
parser.add_argument("--selection", type=str, default="", help="모자이크 처리할 얼굴 번호(쉼표로 구분, 예: 0,2,3, 또는 all)")
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, default="yolov8x-face-lindevs.pt", help="YOLOv8-face 모델 경로")
args = parser.parse_args()
main(args.input, args.output, args.selection, args.model)